Information
Gladiator arena from Roman era unearthed in Turkey
Archaeologists in Turkey have discovered the remains of a "magnificent" Roman-era arena, where up to 20,000 spectators likely cheered and jeered as they watched gladiator matches and wild animal fights, the excavators said.
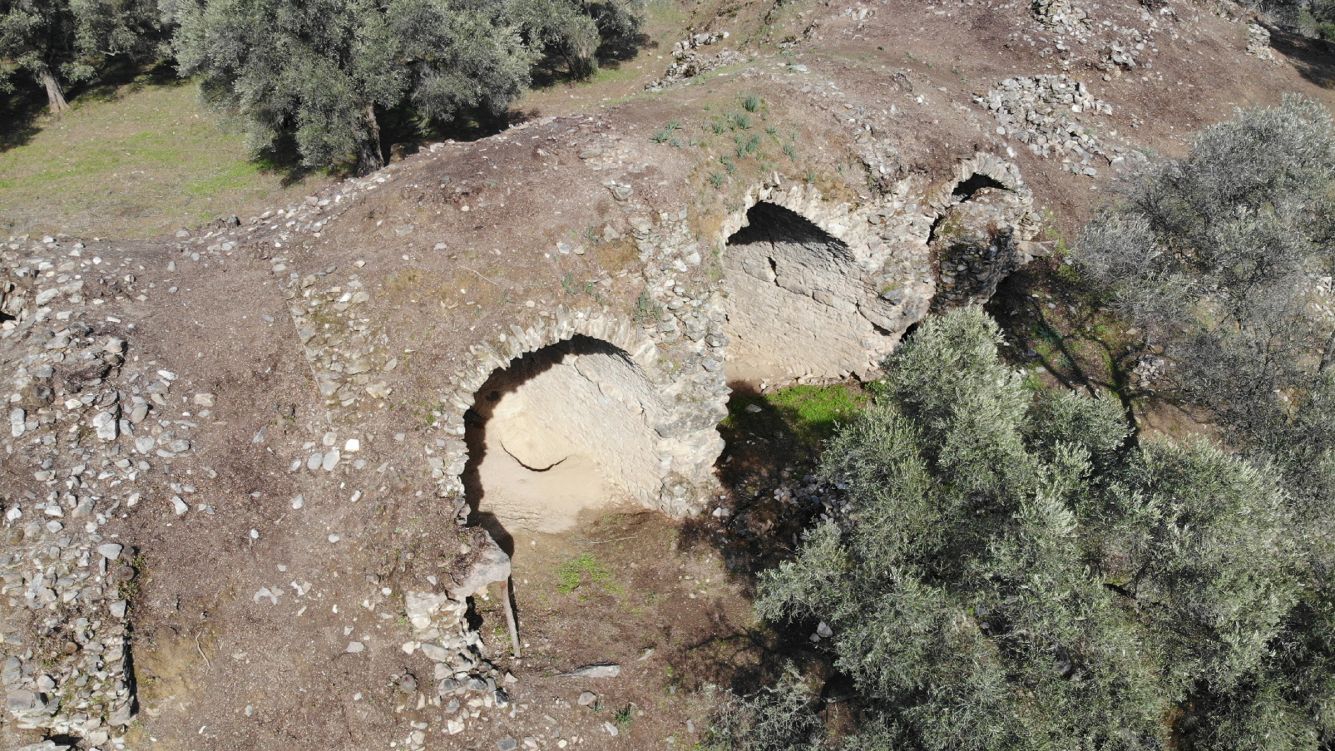
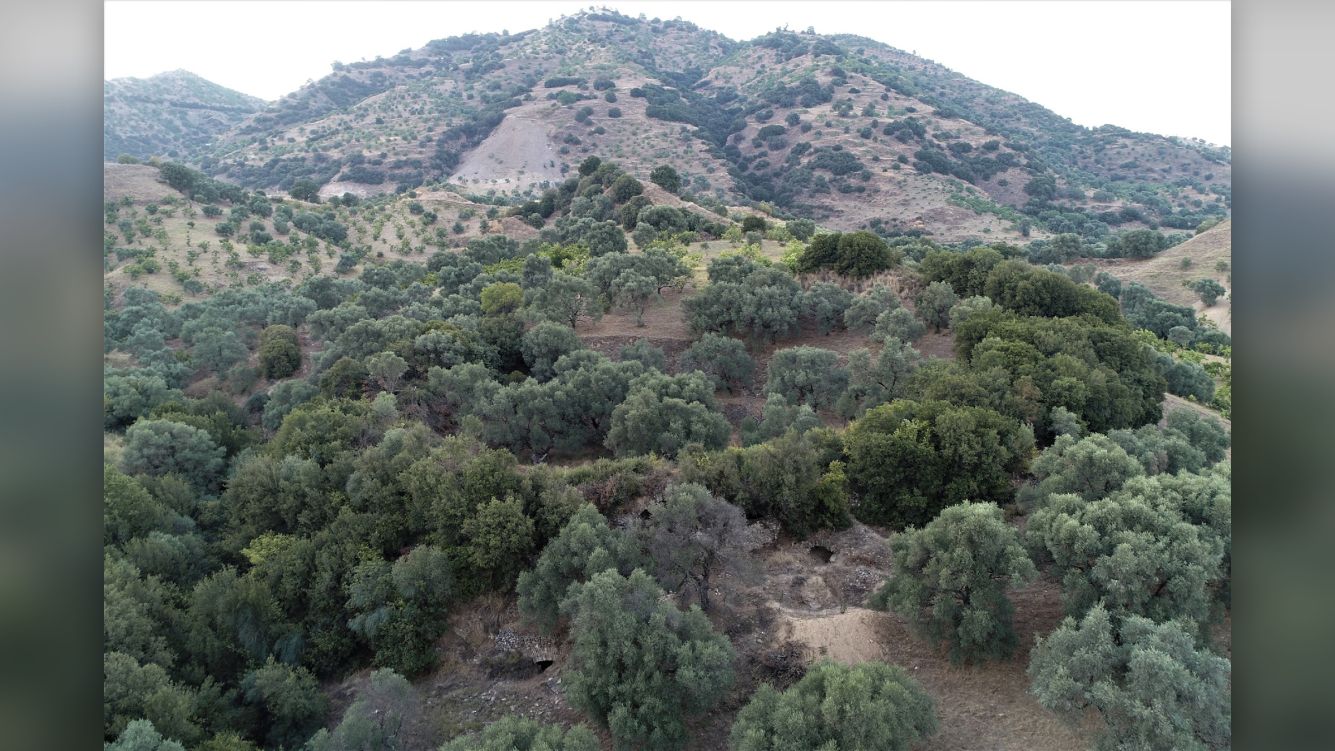
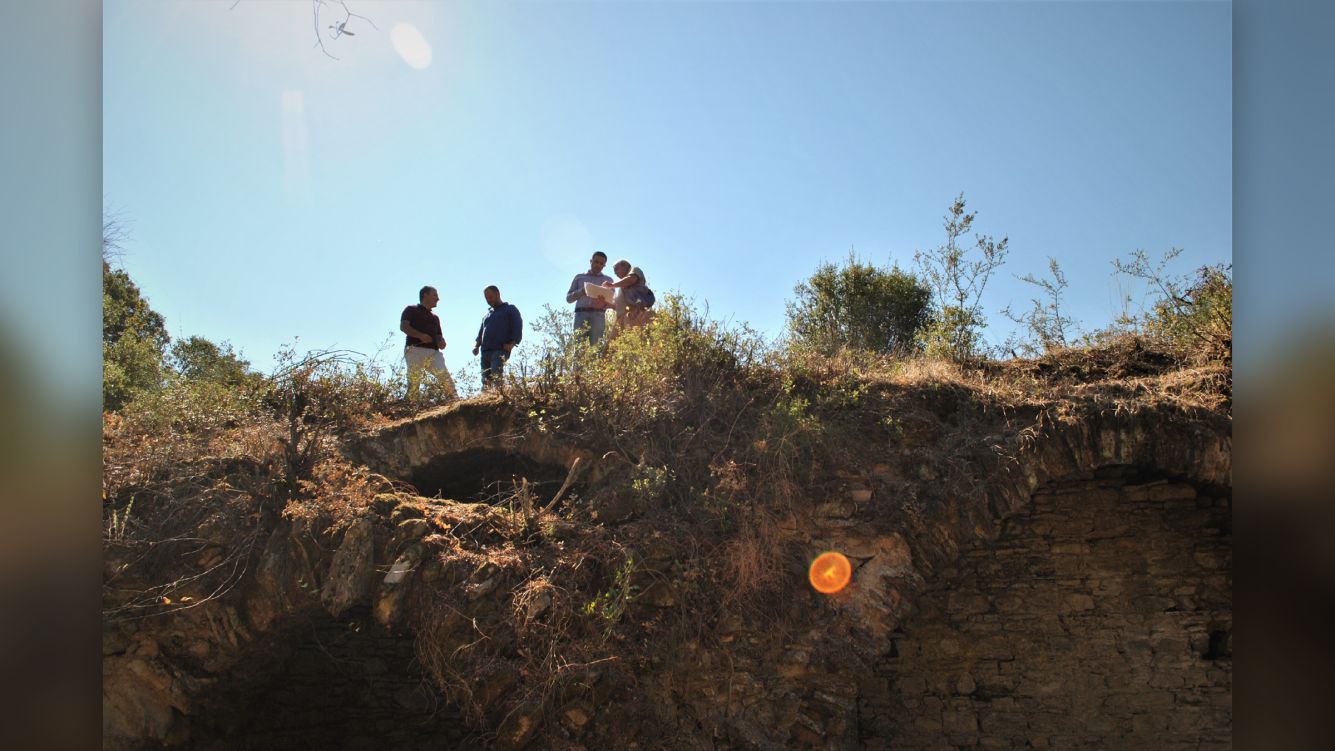
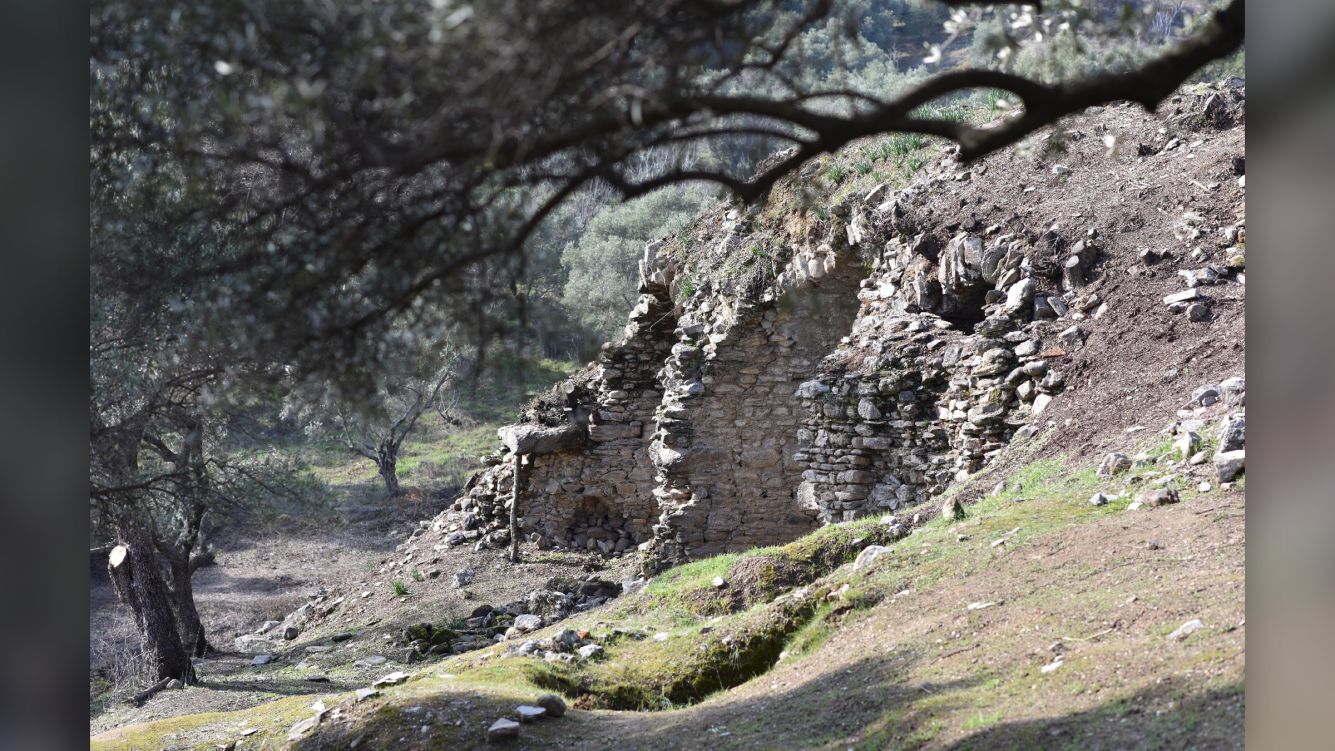
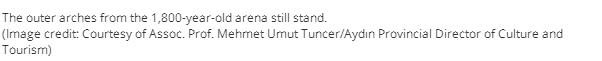
The 1,800-year-old arena was discovered on the rolling hills of the ancient city of Mastaura, in Turkey's western Aydın Province. Its large central area, where "bloody shows" once took place, has since filled with earth and vegetation over the centuries.
"Most of the amphitheater is under the ground," and the part that is visible is largely covered by "shrubs and wild trees," Mehmet Umut Tuncer, the Aydın Culture and Tourism provincial director and project survey leader Sedat Akkurnaz, an archaeologist at Adnan Menderes University in Turkey, told Live Science in a translated email.
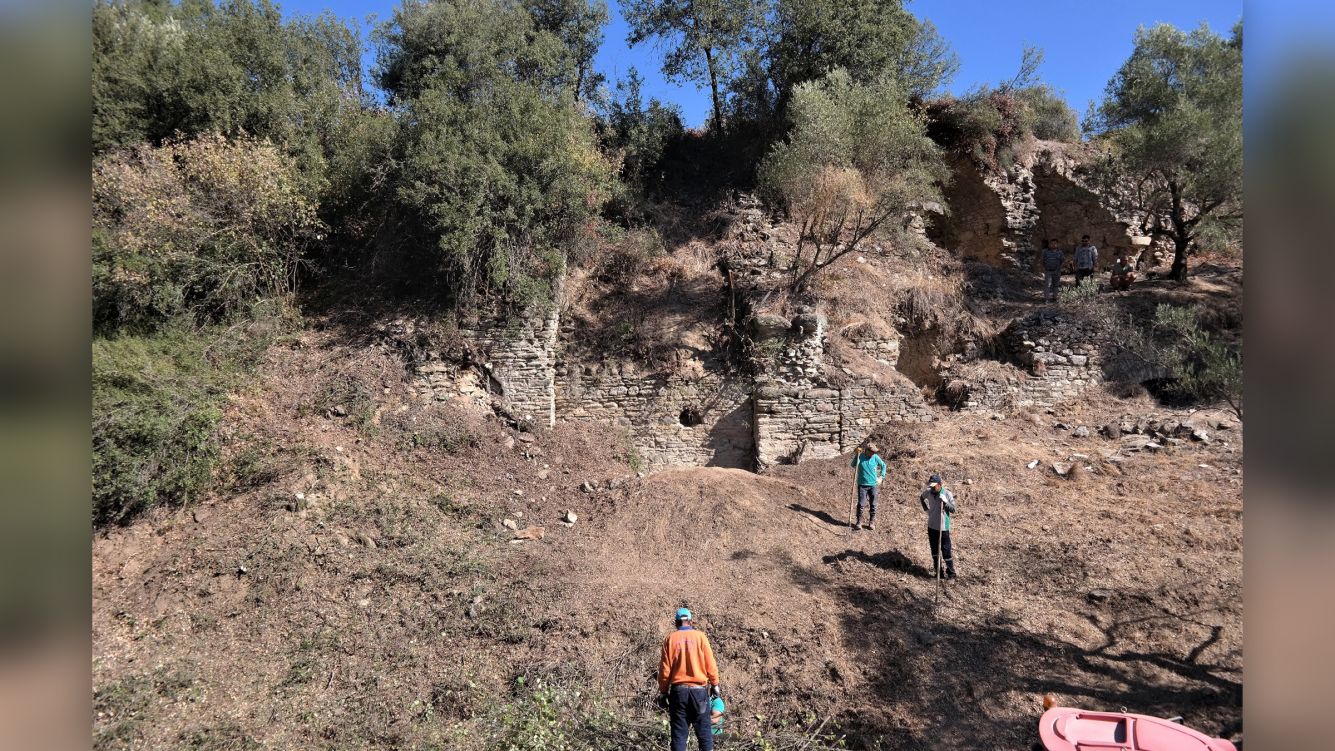
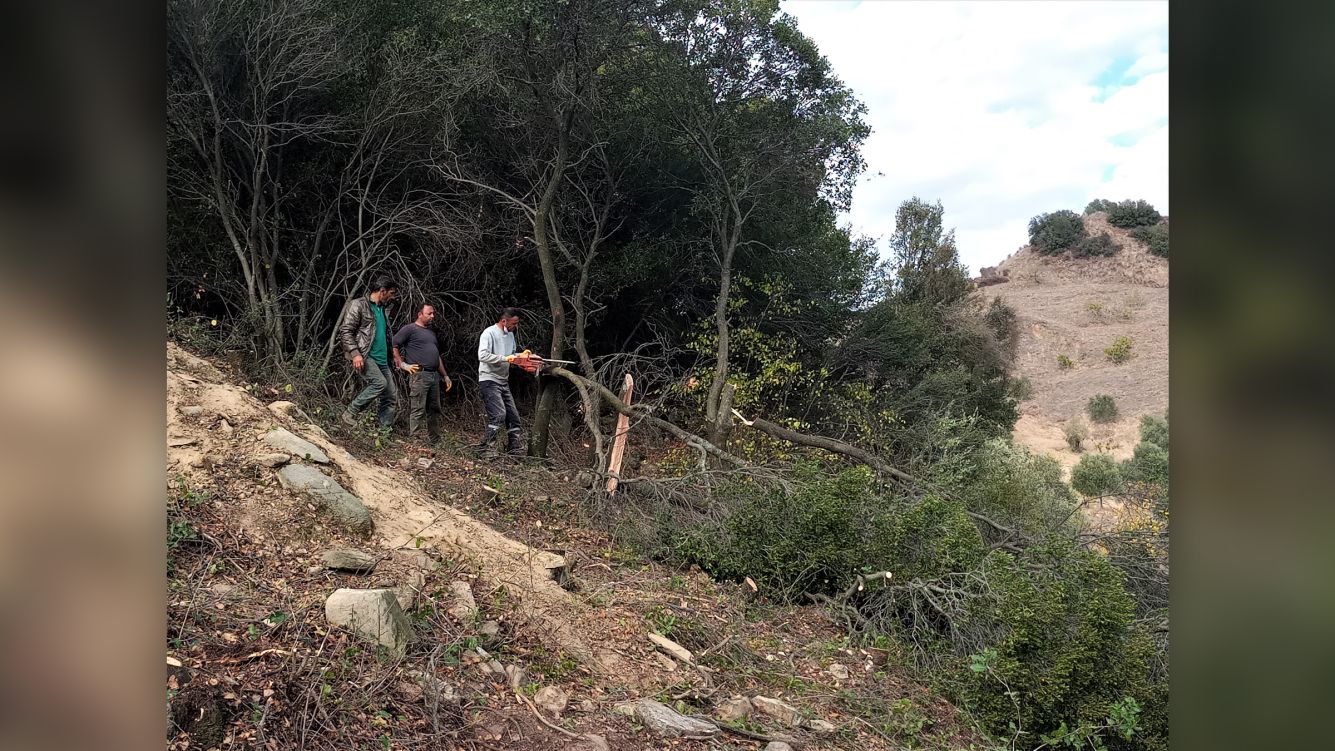
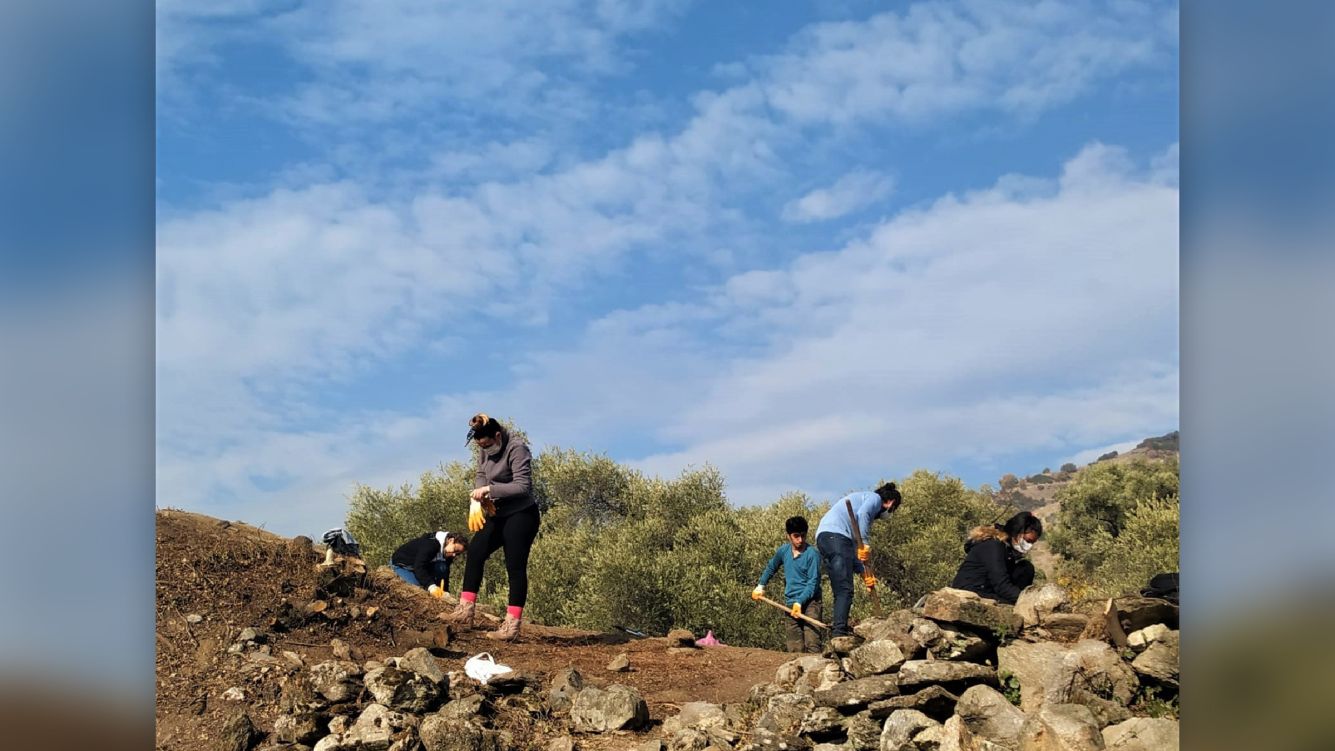
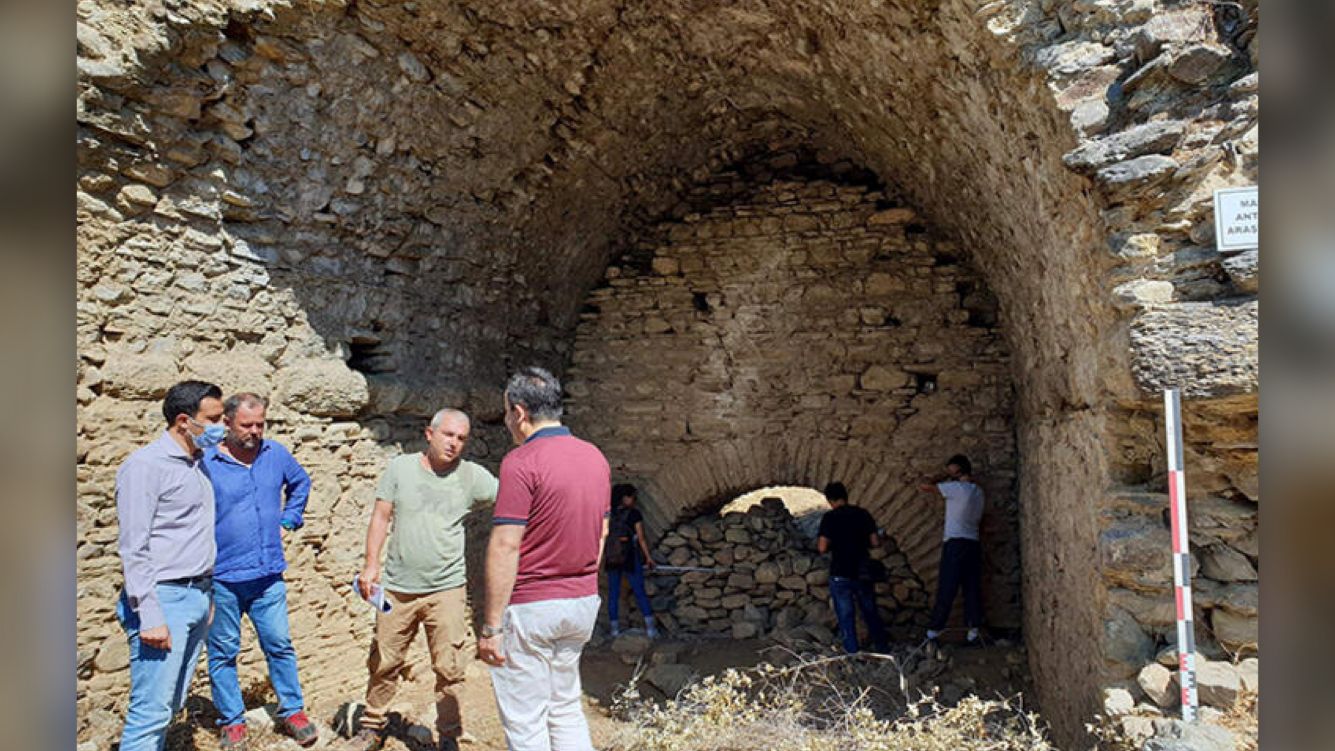
Archaeologists found the arena in the summer of 2020, after they received permission from the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism to conduct archaeological research in the ancient city. After finding immense stonework rising out of the ground, the team immediately began clearing and studying the site. From October to December 2020, they "cut down all the bushes and wild trees," Akkurnaz and Tuncer said. "We started to protect the building against the destruction of nature."
It soon became clear that the arena was old, dating to about A.D. 200, meaning it was built during the Severan Dynasty, which included five emperors who successively ruled from A.D. 193 to 235, they said.
"During this dynasty, the city of Mastaura was very developed and rich," as Roman administrators helped the city grow economically, which led to new stonework and masonry dating to that dynasty, Akkurnaz and Tuncer said. "There is a great increase and variety of Mastaura coins during this period," they added.
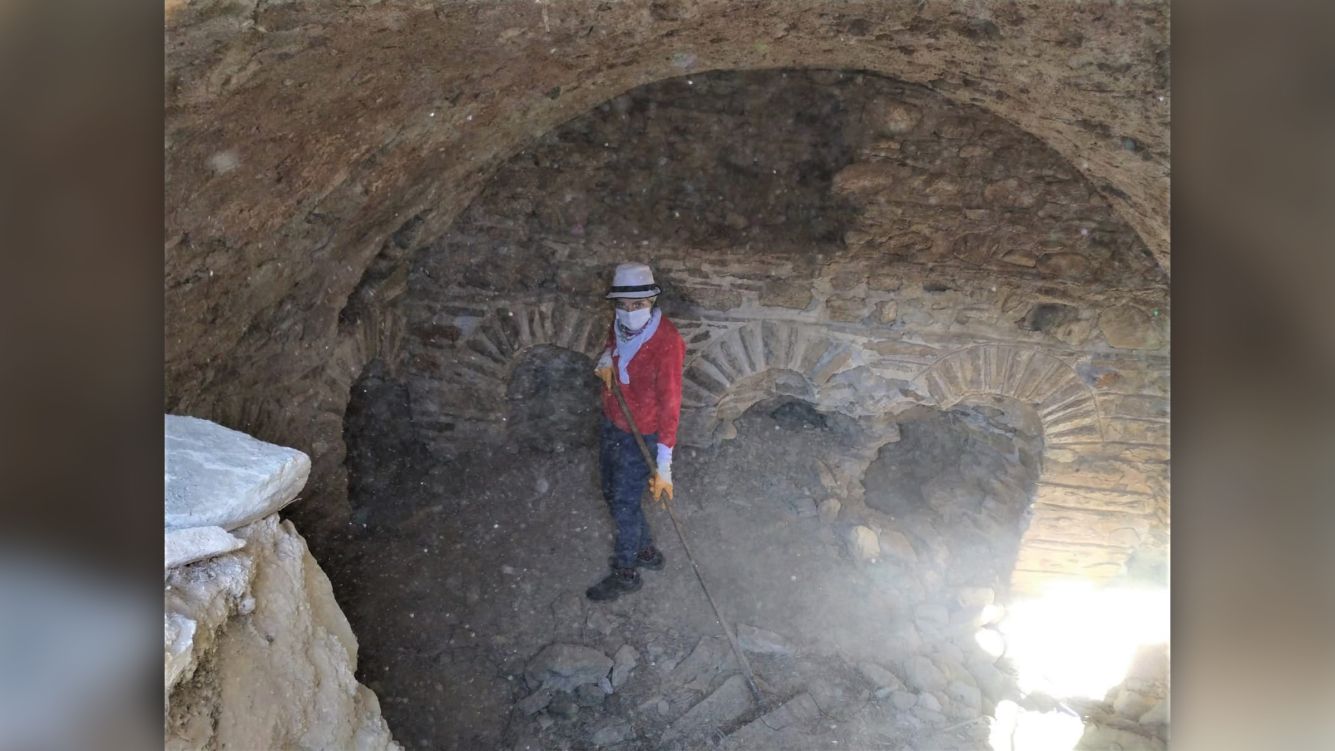
Much of the arena's underground structure is well-preserved. "It is solid, as if it was just built," Akkurnaz and Tuncer said. Many of the structures above ground have crumbled over the years, but it's still possible to find "some of the rows of seats, the arena where gladiators fought and the supporting walls outside the building," they said.
Between 15,000 and 20,000 people could fit into the arena, making it smaller than the famous Colosseum in Rome, which held about 50,000 people, Akkurnaz and Tuncer said. The Colosseum, which was built in about A.D. 70, was larger overall — its outer walls still stand about 157 feet (48 meters) compared with the Mastaura arena's 82-foot-tall (25 m) walls; and the Colosseum's central arena was roughly 285 feet by 180 feet (87 by 55 m), compared with Mastaura's smaller arena of about 131 feet by 98 feet (40 by 30 m), Akkurnaz and Tuncer said.
Mastaura arena's gladiator battles and wild animal fights, which people bet on, however, were likely just as bloody as those at the Colosseum, Akkurnaz and Tuncer said. The arena also had specialized areas, including gladiator waiting rooms and entertainment rooms for private spectators, the archaeologists found.
"There is no previous example of such an amphitheater in Anatolia [also known as Asia Minor] and its immediate surroundings," the researchers said. The arena likely attracted spectators from all over, including from the ancient Western Anatolian cities of Aphrodisias, Ephesus, Magnesia, Miletus and Priene, they said.
"People from neighboring cities were coming to Mastaura town to watch the big events in this building, specially designed for bloody shows," they said.
Going forward, the team is working with the Aydın Archaeological Museum and the Nazilli Municipality, which encompasses Mastaura, to clean and preserve the arena. They plan to address "cracks in the walls of the building" and masonry stones that are falling off the ancient structure. The team has already conserved one of the arena's walls and has started doing laser scans of the structure so they can make a virtual 3D image of it.
After that's done, likely in May, the archaeologists plan to do geophysical surveys above the building so they can "understand what the underground parts of the building are like," Akkurnaz and Tuncer said.
Originally published on Live Science.
Category: English
News
Information
Key words: